Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral disease that primarily affects cloven-hooved livestock and wildlife.
Foot-and-Mouth Disease is a severe, highly communicable disease of cattle, pigs, sheep, goats and deer. It is caused by one of the …
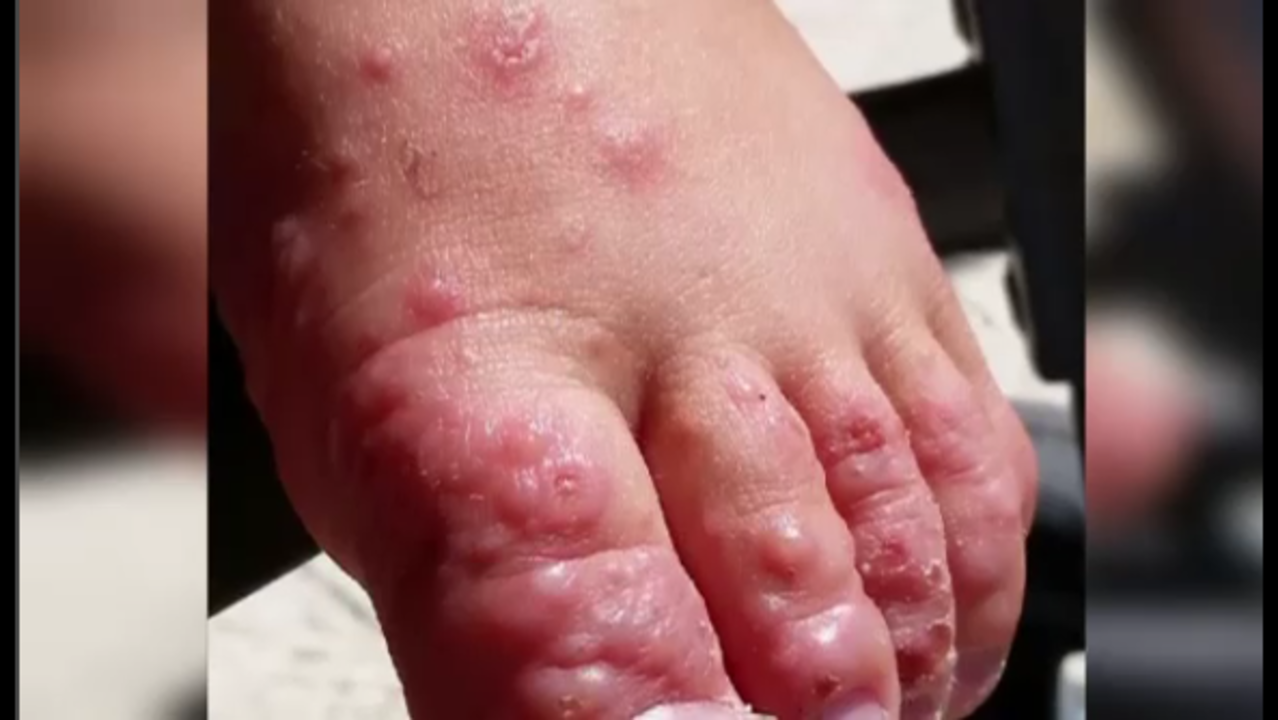
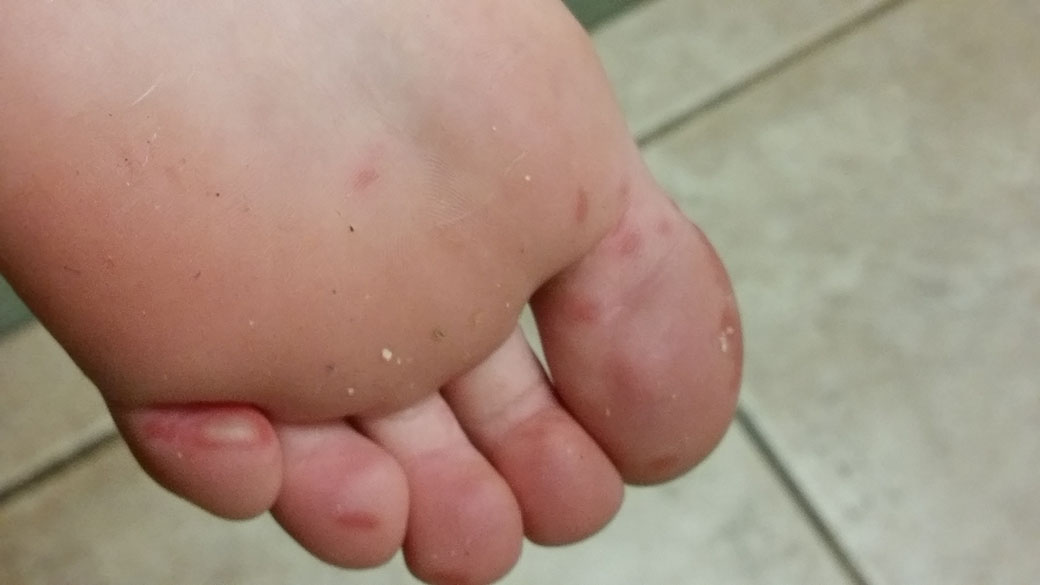
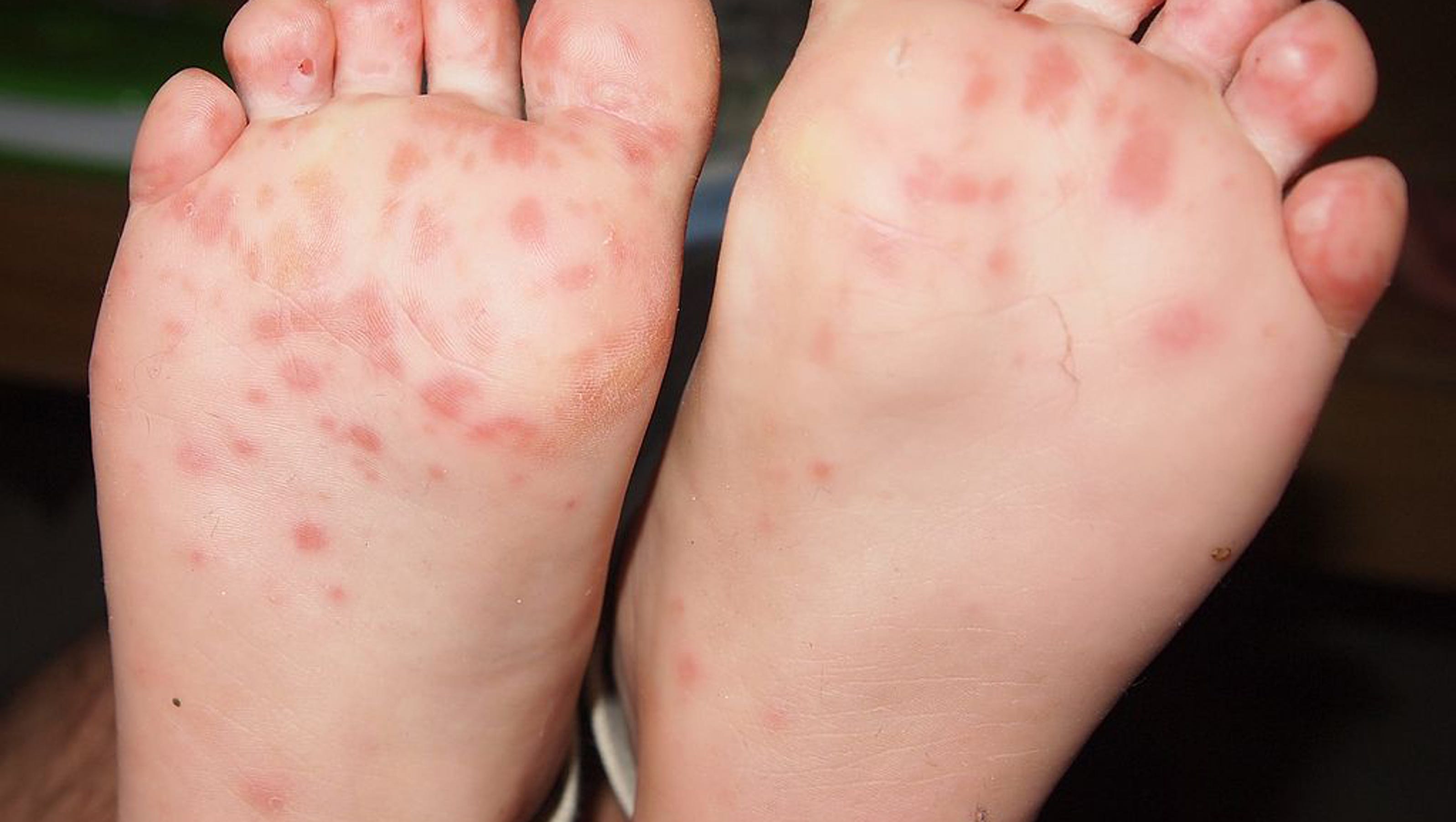
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a highly contagious viral infection that’s common in ren. This virus is marked by blisters or sores in the mouth …
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is generally caused by coxsackievirus A-16, which is a member of the enterovirus family.; There are other types of enteroviruses that can cause the symptoms as well, but these are less common.
![]()
Overview. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a common illness of infants and ren. In infants, it starts with fever, fussiness, and poor appetite.
![]()

Hand, foot, and mouth disease is common in infants and ren. It usually causes fever, painful sores in the mouth, and a rash on the hands and feet. Most infected people recover in a week or two. Wash your hands often and practice good hygiene to reduce your risk of infection. Hand, foot
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is caused by viruses that belong to the Enterovirus genus (group). The viruses are found in the nose and throat secretions, saliva, fluid in blisters, and stool of infected persons and spread from person to person, often when infected persons touch objects and surfaces that are then touched by others.


Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common infection caused by a group of viruses. It typically begins with a fever and feeling generally unwell. This is followed a day or two later by flat discolored spots or bumps that may blister, on the hands, feet, and mouth, and occasionally buttocks and groin.
Foot-and-mouth disease or hoof-and-mouth disease (Aphthae epiticae) is an infectious and sometimes fatal viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed s, including domestic and wild bovids.

Parents often ask “Is hand foot and mouth disease contagious?” The answer is yes. This article outline how, for how long & who is most vulnerable.